VHRR
VHRR/2 is a modified version of the VHRR heritage imagers flown on INSAT-2A, -2B, and -2E. The VHRR observes in VIS, water vapor and TIR bands providing a spatial resolution of 2 km in VIS band and 8 km for the rest. VHRR was developed by SAC (Satellite Application Center), Ahmedabad, India. The instrument operates in three scanning modes:
- Full frame mode (20° North-South x 20° East-West), minimum in about 33 minutes covering the entire Earth disk
- Normal frame mode (14° N-S x 20° E-W), minimum in about 23 minutes
- Sector frame mode in which the sector can be positioned anywhere in steps of 0.5° in the N-S direction to cover 4.5° N-S x 20° E-W. This mode is particularly suited for rapid, repetitive coverage during severe weather conditions like a cyclone.
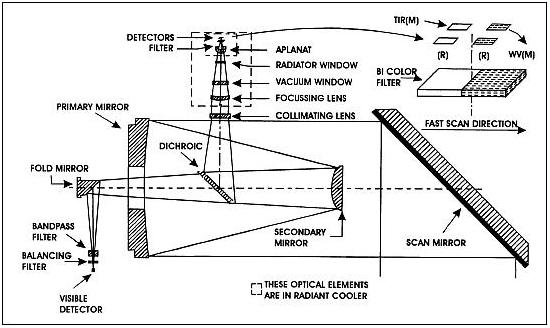
The nominal frame repetition rates are: 40, 30 and 20 minutes respectively. VHRR is an opto-mechanical system (whiskbroom type imager). The incoming solar radiation is reflected onto a Ritchey-Chretien telescope of 20 cm aperture by a beryllium scan mirror mounted at 45° to the optical axis. The optical system includes a gold-film dichoric beam-splitter that transmits visible light energy and reflects WV/TIR energy, so that the radiation from the Earth is channelized to the visible and IR focal planes simultaneously.
The visible band detector configuration consists of two staggered arrays of four silicon photodiodes each; while two sets of mercury-cadmium telluride (MCT) detector elements operating nominally at 100-110 K sense the WV/thermal radiation. The scan mirror is mounted on a two-axis, gimballed scan mechanism system to generate a 2-D image by sweeping the detector instantaneous field of view (FOV) across the Earth's surface in east to west (fast scan) and north to south (slow scan).
Imaging modes of the VHRR instrument
| Imaging mode | Coverage | Repeatability |
|---|---|---|
| Full scan | 20° N-S and 20° E-W | 33 min |
| Normal scan | 14° N-S and 20° E-W | 23 min |
| Sector scan | 4.5° N-S and 20° E-W | 23 (3 times) |
Imaging modes of the VHRR instruments
| Channel | No of detectors | MTF (Modulation Transfer Function) | Dynamic range | Noise performance |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| VIS | 4 +4 redundant | > 0.23 approx. | 0-100% albedo | 6 : 1 min at 2.5% albedo |
| Water Vapor (WV) | 1 + 1 redundant | > 0.21 approx. | 4-340 K | 0.25 K at 300 K |
| TIR | 1 + 1 redundant | > 0.21 approx. | 4-320 K | 0.5 K at 300 K |
Schematic illustration of the VHRR instrument
VHRR Instrument
| Spectral band: VIS Spectral band: TIR Spectral band: MWIR (Water vapor) |
0.55 - 0.75 µm; Integrated out-of-band response <3% Inter detector mismatch < 5% 10.5 - 12.5 µm; Integrated out-of-band response <3% Out-of-band response peak < 0.1% 5.7 - 7.1 µm |
|
| Spatial resolution VIS Spatial resolution TIR and MWIR |
56 µrad (or 2 km x 2 km) 224 µrad (or 8 km x 8 km) |
|
| Radiometric performance: SNR Radiometric performance: NEDT |
> 6 for VIS at 2.5% albedo < 0.25 K at 300 K for IR channel |
|
| Dynamic range of TIR/MWIR channels Dynamic range of VIS channel |
4-340 K 0-100% |
|
| Misregistration between VIS and IR | <56 µrad | |
| Modulation Transfer Function (MTF) | > 21% for IR and TIR; >23% for VIS channel | |
DRT (Data Relay Transponder)
The DRT (Data Relay Transponder) is part of a DCS (Data Collection System) of ISRO. The objective is to collect data from unattended meteorological platforms in the ground segment. DRT receives receives signals from unattended weather data collection platforms and retransmits them to the central station. The data from these payloads are being used for comprehensive weather status and forecasting.
RF communication of DRT: Uplink frequency = 402.75 MHz; downlink frequency = 4506.05 MHz; bandwidth =± 100 kHz; EIRP = 21 dBW (min).
Note: MetSat-1 does not carry SAS&R (Satellite Aided Search and Rescue) system. In the INSAT-2 series, the INSAT-2A and -2B satellites carried SAS&R transponders as well as DRTs (Data Relay Transponders). According to ISRO information, INSAT-3A (launch April 9, 2003) and INSAT-3D (to be launched subsequently), will carry SAS&R and DRT payloads.